You must obtain omega-3 fatty acids from dietary sources like fish and nuts or supplements like fish oil since they are essential fatty acids that your body cannot make on its own. So, people always search for all the benefits and precautions of Omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are necessary for strong cell membranes. They also provide your body with energy and support the healthy operation of your immune, endocrine, and cardiovascular systems. But, before intake people should be well aware of the health benefits and precautions of Omega-3 fatty acids.
Researchers discovered that smoking presented a reliable indicator of a reduced life expectancy, just as four other types of fatty acids, including omega-3, did. Even a quintile rise in these fatty acids—say, from the 0–20% range to between 20–40%—is linked to a favorable shift. Salmon and other fatty fish are the main sources of omega-3s, but they are also available as supplements. Here, we will explain all the health benefits and precautions of Omega-3 fatty acids.
Intake of Omega-3s helps in the following ways:
- Lower your blood pressure
- May reduce levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol
- Rheumatoid arthritis treatment
- Your blood’s concentration of omega-3 fatty acids may be a good indicator of mortality risk.
- Your life could be extended even a little by increasing your consumption of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Improved cardiac health
- Fewer arthritic flare-ups and pain
- Decreased risk of some malignancies
- Enhanced cognitive function in mild Alzheimer’s disease patients
Table of Contents
Omega-3 Deficiency
When intakes fall below recommended levels over time, when someone has a particular risk factor for lower-than-normal levels, or when someone has a specific reason why they cannot digest or absorb omega-3s, some persons may develop omega-3 insufficiency.
Some symptoms of an omega-3 shortage can appear, and they frequently do so in the skin. Rough, scaly skin and dermatitis, a persistent skin ailment that causes itching, redness, and inflammation, are examples of symptoms.
Food High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
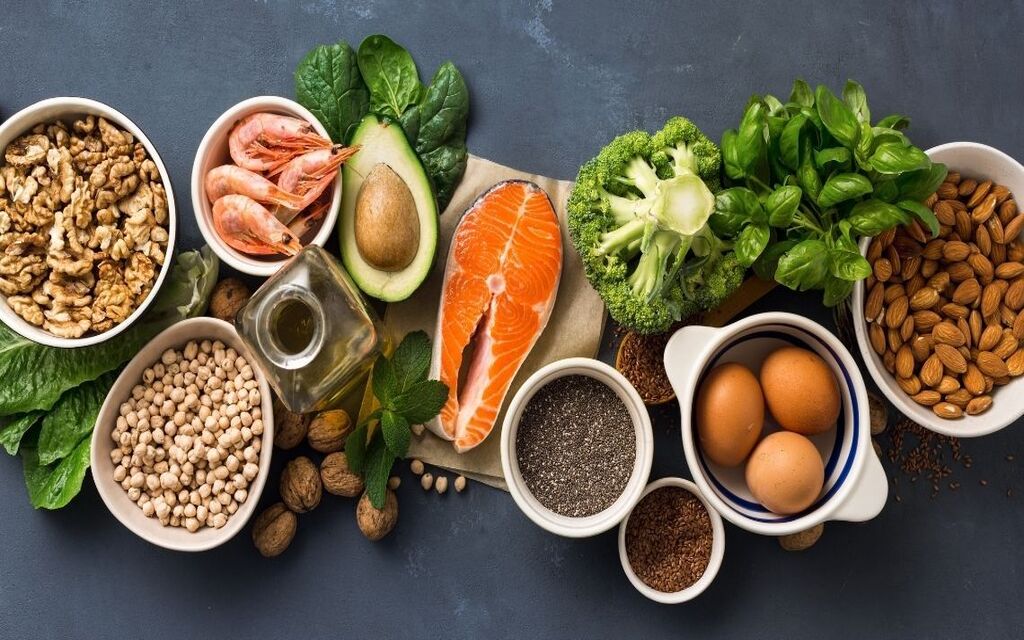

- Salmon, Tuna, Shrimp, Oysters
- Walnuts
- Dark chocolate
- Sardines, Kidney beans
- Fish liver oils, such as cod liver oil and krill oil
- Algae, Algal oil
- Soybean oil, Flaxseed oil
- Chia seeds, Flaxseeds
Benefits of Omega-3
The potential benefits of omega-3 include the following:
Omega-3 for Eye Health
The main fatty acid that constitutes the retina of the eye is an omega-3 fatty acid called DHA. DHA is necessary for a fetus’s and an infant’s proper eye development during pregnancy and while nursing.
Your eye health depends on it throughout your entire life. According to research, consuming enough omega-3s lowers the chance of developing eye conditions including age-related macular degeneration.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Reduce Inflammation
According to research, omega-3 fatty acids are crucial in reducing inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids are converted into antioxidants and anti-inflammatory substances by the body when they are broken down. Thus, it aids in reducing inflammation and offers cell protection.
Inflammation is thought to contribute to the onset of a number of chronic diseases, including cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis. Therefore, lowering inflammation may help you experience fewer of these chronic diseases’ symptoms.
Omega-3 and Heart Health
One of the main causes of death is cardiovascular disease. Omega 3 fatty acids may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and enhance critical heart health indices.
For Better Brain Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for a child’s developing brain during pregnancy and infancy. The primary fatty acid utilized to build the brain’s cell membranes is DHA. And the first six years of life are when the majority of brain development takes place.
According to research, EPA and DHA are both equally effective at increasing the amount of DHA in the brain. Therefore, getting enough of these nutrients while pregnant, nursing, or growing up is crucial.
Omega-3 for Immunity
It also helps to boose your immunity. Chronic inflammation has the potential to initiate or exacerbate a number of autoimmune illnesses. Decreased inflammation may aid in symptom management and disease progression. The immune system’s response to an infection, illness or injury includes inflammation. The immune system misidentifies healthy cells as abnormalities and assaults them in autoimmune illnesses.
Protect Against Alzheimer’s Disease
Cognitive decline and changes in brain health are frequent side effects of aging. Many researchers suggest that omega-3 fatty acids may maintain brain function as we age and reduce the chance of Alzheimer’s disease.
According to a comprehensive review, taking omega-3 supplements may help persons with early-stage Alzheimer’s disease perform better cognitively.
Helps to Remove Cancer Treatment Side Effects
Both the growth of tumors and the negative effects of cancer treatment are influenced by inflammation. On the question of whether omega-3 fatty acids can genuinely help prevent malignancies like prostate cancer, research is conflicting.
However, a 2013 study found that adding omega-3 supplements to chemotherapy may help patients fare better by lessening inflammation and the negative effects of the drug.
May Reduce Depression
By reducing the risk of developing some mental health issues like schizophrenia and depression, omega-3 fatty acids may also benefit the health of your brain. A 2019 study discovered that taking omega-3 supplements with EPAs reduced the symptoms of depression.
Omega-3 and Weight Loss
Omega-3 fatty acids also help in weight loss. It helps to lose your body fat by reducing hunger and appetite. However, according to studies these effects may not apply to everyone.

Reduced Risk of Age-related Macular Degeneration
Changes in the risk of early death have previously been linked to omega-3s. According to a study published in Nature Communications, the presence of fatty acids can cut the risk of early mortality by 13%, mainly because they lower the risk of acquiring cardiovascular disease and possibly even some types of cancer.
Another fatty acid called omega-6, however, can only be helpful if it is ingested in moderation because excessive amounts might lead to inflammation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Side Effects & Precautions
According to a study that was published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, having higher amounts of omega-3 fatty acids in your blood can extend your life by up to five years.
Some medicines and omega-3 fatty acids can interact. For instance, taking omega-3s along with warfarin (coumadin) or other anticoagulants (blood thinners) may make it take longer for your blood to clot. Therefore, before beginning an omega-3 supplement, see a healthcare provider if you use any drugs, especially blood thinners.
The American Heart Association and several doctors advise eating one to two portions of fatty fish per week. Cooked fish weighing 1/2 ounces makes up one dish.
A fish oil supplement with roughly 1 gram of omega-3 fats is an option if you dislike eating fish. You shouldn’t, however, increase your dose more without first talking to your doctor. A person may bleed and bruise more easily if their blood platelet levels are low due to high quantities of omega-3 fatty acids.
Conclusion:
Omega-3 fatty acids are necessary nutrients that can be found in food or dietary supplements. Omega-3s come in three different forms: DHA, EPA, and ALA. Omega-3 fatty acids may help to protect the heart, brain, and eyes, as well as reduce the risk of various chronic diseases. To lower the risk of heart disease, the AHA advises eating one to three servings of fish per week. Additionally, when pregnant or nursing, the AAP advises consuming one to two servings of fish each week.
Also Read: What to Do in Constipation?
Image Source: Yandex.com